© NEC
- Remote medical examination trials part of the government’s 5G test programme
- Utilised a massive-element 28GHz band AAS base station system
- Real time communication and sharing of images taken by a 4K camera
- System could be used for providing emergency medical care
NEC has announced its contributions to field trials in remote medical examinations using 5G. NEC provided a base station system as part of comprehensive demonstration carried out by NTT Docomo, the Wakayama Prefectural Government, and Wakayama Medical University. The trial was conducted by NTT Docomo under a project commissioned by Japan's Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications to examine the technical specifications for 5G systems that can realise data speeds exceeding 10Gbit/s in densely populated areas.
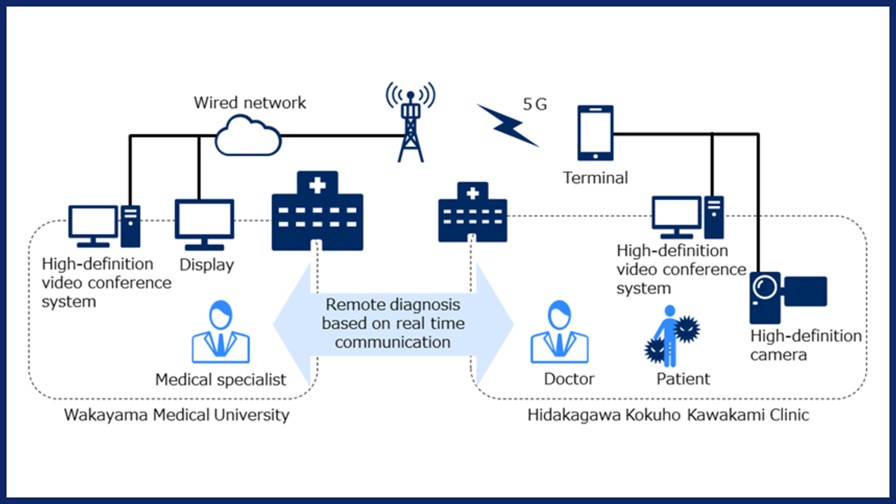
Wakayama is a mountainous, sparsely populated region of Japan, with limited access to advanced medical institutions, which are often understaffed and whose resident doctors are frequently required to see patients outside of their field of expertise. The local government created a remote medical support system using video conferencing that connects 13 regional medical institutions to Wakayama Medical University, allowing doctors to receive advice from specialists. However, the system frequently experienced problems, including unclear images and transmission delays.
In order to address these issues, verification tests have been conducted with an optical cable to establish a remote medical examination service using 5G to connect Wakayama Medical University and Hidakagawa Kokuho Kawakami Clinic, over a distance of about 30km. As part of this test solution, NEC set up a massive-element Active Antenna System (AAS)base station system operating over the 28GHz mmWave band.
"Ultra-high-speed 5G communications are often associated with the entertainment industry, however, these trials showed us that 5G can play a role in solving social issues, such as reducing regional disparities in the delivery of health care,” said Jun Mashino, Senior Research Engineer, 5G Radio Access Network Research Group, 5G Laboratory, NTT Docomo. “We plan to create new business models and value by continuing to take advantage of 5G technologies in collaboration with ICT vendors, and a wide variety of companies and organisations in the near future.”
NEC reports that 5G transmission has enabled real time communication and sharing of images taken by a 4K close-up camera, high-definition echocardiographic video and MRI images using a 4K video conference system. High-definition, large-screen monitors made it possible to easily view the condition of a subject in clear detail. It also became possible to communicate with patients more personally, due to the low latency.
"The remote medical examinations system, where valuable advice can be delivered by medical specialists, will likely become a reliable support system for inexperienced doctors who are newly dispatched to remote areas,” said Dr Takashi Yamano, Department of Cardiovascular Medicine Community at the Wakayama Medical University. “I also believe that the system can be utilised for providing emergency medical care, such as by using small-sized echo cameras to transmit high-speed video images of patients at disaster sites or at the site of an accident.”
"In the field trials, it was as if the medical specialist at the prefectural medical university was right there next to me as we watched the same video of the patient's affected area,” said Dr Naoki Hirabayashi, Director of the Hidakagawa Kokuho Kawakami Clinic. “Getting the opinion of a medical specialist provides patients with the advantage of a highly reliable examination, while the doctors are provided with the opportunity to acquire specialised knowledge.”
NEC's massive-element AAS base station system adopts a fully digital control system, which enables simultaneous beamforming in multiple directions from a single massive-element AAS unit. This then efficiently implements high-speed and high-capacity communication without interfering with adjacent users through spatial multiplexing.
“We are honoured to have contributed to the efforts to improve medical services in sparsely populated, mountainous areas by utilising high-speed and large-capacity 5G wireless technology,” said Seiji Kondo, GM Wireless Access Solutions Division, NEC Corporation. “We will continue to improve the performance of 5G technology and contribute to the provision of new medical services in cooperation with NTT Docomo and Wakayama Medical University.”
Email Newsletters
Sign up to receive TelecomTV's top news and videos, plus exclusive subscriber-only content direct to your inbox.




