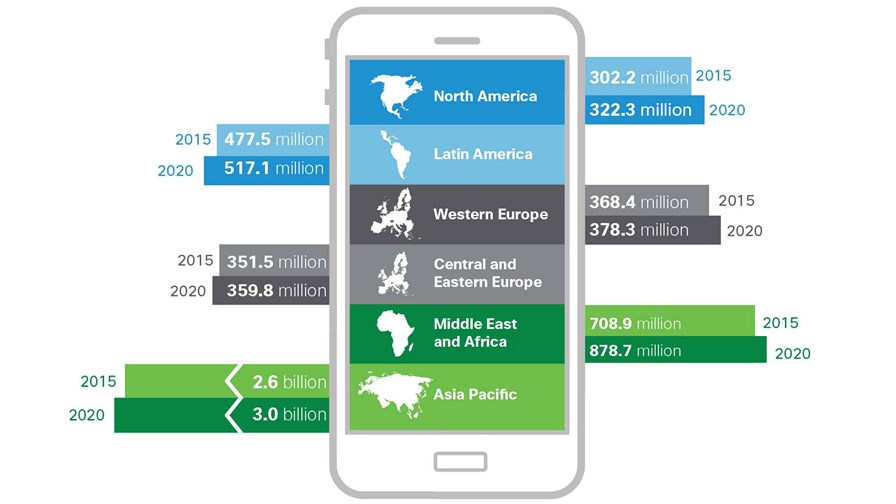
Growth in regional mobile users 2015-2020 © Cisco
- Latest annual VNI Mobile Forecast released by Cisco
- Growth in mobile data predicted CAGR of 52.6 per cent from 2015 to 2020
- 70 per cent of global population will be mobile users by 2020
- Average global mobile network speeds to reach 6.5Mbit/s by 2020
Cisco has published the latest edition of its Visual Networking Index (VNI) global mobile data traffic forecast, covering the period from 2015 to 2020. It believes that by 2020, there will be 5.5 billion mobile users, representing 70 percent of the global population. This increase in user growth – which is twice as fast as that of the global population – will increase mobile data traffic eight-fold over the next five years.
“Mobility is the predominant medium that’s enabling today’s global digitization transformation,” said Doug Webster, VP of service provider marketing, Cisco. “Future mobile innovations in cellular, such as 5G, and Wi-Fi solutions will be needed to further address new scale requirements, security concerns, and user demands. IoT advancements will continue to fuel tangible benefits for people, businesses, and societies.”
Naturally, Cisco predicts that mobile video will have the highest growth rate of any mobile application. It believes that by 2020, over 75 per cent of the world’s mobile data traffic will be video. Here are some of the report’s other statistical highlights for 2020:
- Global mobile data traffic will reach 30.6 exabytes per month – up from 3.7 exabytes in 2015
- Annual global mobile data traffic will reach 366.8 exabytes – up from 44.2 exabytes in 2015
- The forecast mobile data traffic for 2020 is equivalent to 120-times more than all global mobile traffic generated 10 years ago in 2010
- From 2015 to 2020, global mobile data traffic will grow two times faster than global fixed IP traffic
- 55 per cent of total mobile data traffic will be offloaded, compared to 51 per cent in 2015
- There will be 11.6 billion mobile-ready devices and connections (8.5 billion personal mobile devices and 3.1 billion M2M connections) – up from the 7.9 billion total in 2015
- Globally, 67 per cent of mobile devices and connections will be 'smart' – up from 36 per cent in 2015
- 98 per cent of mobile data traffic will come from these 'smart' devices – up from 89 per cent in 2015
- However, smartphones, laptops, and tablets will drive about 92 per cent of global mobile data traffic – which is actually down from 94 per cent in 2015, due to the positive impact of M2M/IoT
Mobile technologies
Over the next five years, Cisco believes that average global mobile network speeds will increase by a factor of 3.2 from 2015 to reach 6.5Mbit/s by 2020, with increased 4G adoption the primary catalyst for mobile speed improvements. By 2020, 4G connections will account for 40.5 per cent of all mobile connections – up from 13.7 per cent in 2015, with 3G also up slightly to 38.7 per cent.
Cisco continues to struggle with its IoT nomenclature (don’t we all), but this report specifically refers to M2M, with a particular focus on wearables as a sub-category of M2M (no, we are not quite sure of the logic, but neither are we convinced by the ‘Internet of Everything’ terminology Cisco likes to use).
However, by 2020, Cisco predicts that M2M connections will represent 26.4 percent of mobile-connected devices, an increase from 7.7 percent last year. These connections will generate 6.7 per cent of total mobile traffic by 2020, up from 2.7 per cent in 2015. And looking at wearbles, sales are expected to grow six-fold from 2015 to 2020, when there will be more than 600 million wearable devices in use.
Looking at WiFi, the report shows that hotspot rollout is increasing. Globally, the total number of WiFi hotspots will grow seven-fold from 2015 to 2020 to reach 432 million units. The use of WiFi to offload traffic will also increase. In 2015, monthly WiFi offload traffic (3.9 exabytes) exceeded monthly cellular traffic (3.7 exabytes) for the first time. By 2020, 38.1 exabytes of WiFi offload traffic will be generated each month, continuing to exceed the projected monthly cellular traffic 30.6 exabytes.
WiFi will also play a more prominent role in voice communications. Whilst previous voice over WiFi (VoWi-Fi) offerings had limitations that affected adoption and end-user experiences, the latest carrier-grade VoWi-Fi services can be delivered to non-SIM devices, such as WiFi-only tablets. Therefore, Cisco predicts that:
- By 2016, VoWi-Fi will exceed VoLTE in the number of minutes used per year
- By 2018, VoWi-Fi will exceed VoIP in the number of minutes of used per year
- By 2020, VoWi-Fi minutes of use will account for 53 per cent of all mobile IP voice traffic
- Also by 2020, the number of WiFi-capable tablets and PCs (1.7 billion) will be more than three times the number of cellular-capable tablets and PCs (548 million).
Email Newsletters
Sign up to receive TelecomTV's top news and videos, plus exclusive subscriber-only content direct to your inbox.




